The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping numerous aspects of our lives, and higher education is no exception. The generation of students entering universities today will witness more technological change than ever before. Yet, how can we help our teachers —the guides of this generation— be better prepared for this evolving landscape? To this aim, HKU TALIC presented a series of edTech and AI workshops on emerging technologies with a focus on practical strategies and resources. The workshops were created to provide teachers and the university community more options to enhance student learning, and to cultivate AI literacy and ICT skills. The first workshop held in Spring 2024 focused on the power of prompt engineering, as well as providing tactics and practical examples in AI prompting for teaching practice.
Harnessing the Power of HKU ChatGPT Service
HKU ITS provides staff and students with the ChatGPT and DALL∙E web apps (https://chatgpt.hku.hk/), which are powered by Microsoft’s Azure OpenAI services to improve teaching and learning effectiveness, productivity, and the overall educational experience, The recently released DeepSeek-R1 and DeepSeek-V3 models, as well as models like GPT-4, GPT-4o, and GPT-3.5, are all included in the ChatGPT online app.
How does the ChatGPT web application react to user input? Generally, the AI chatbot produces a response when users input a prompt. Additionally, the ChatGPT web app organizes discussion history into many “topic” groups. In contrast to more basic chatbot models, newer chatbots permit content preservation and more complex, multi-turn interactions.
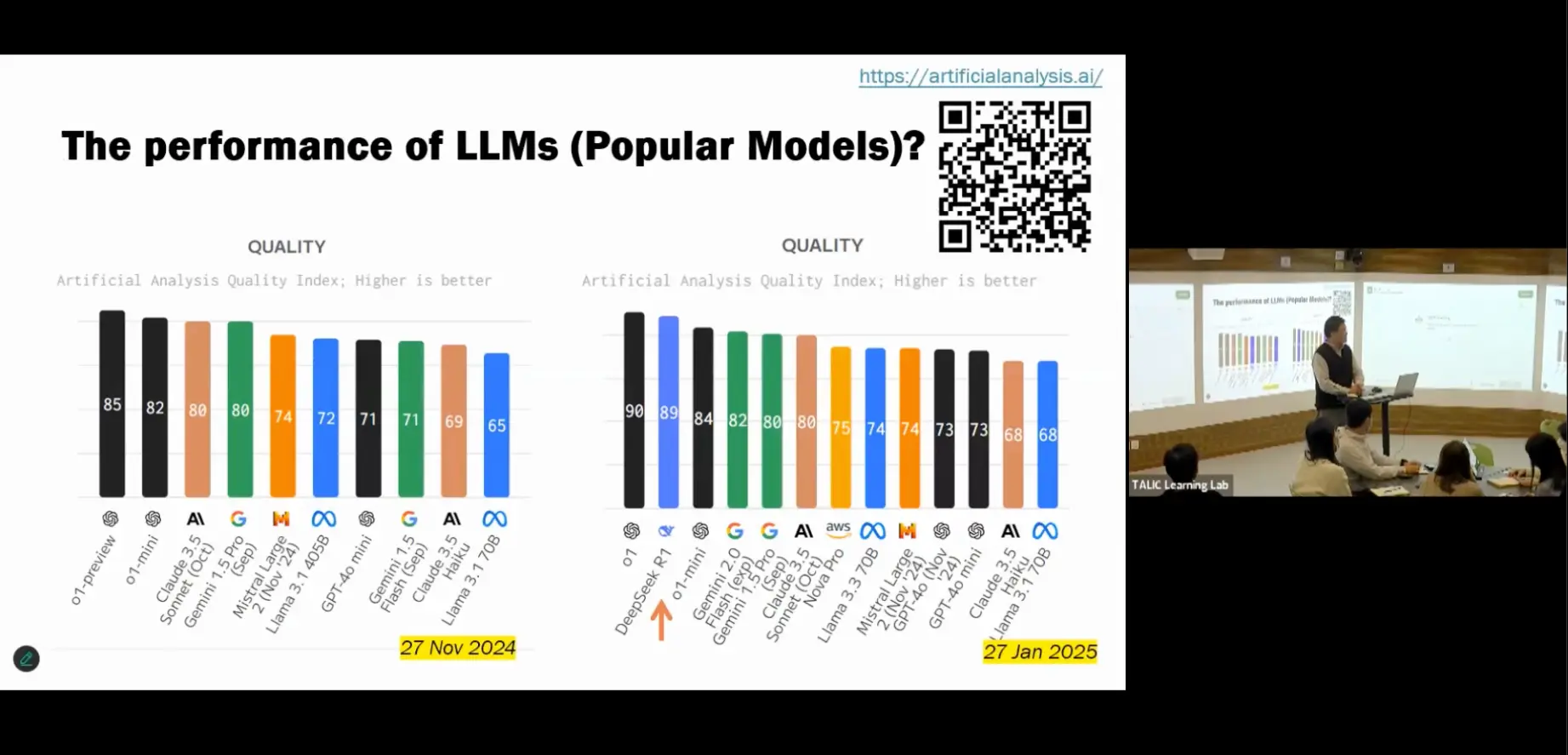
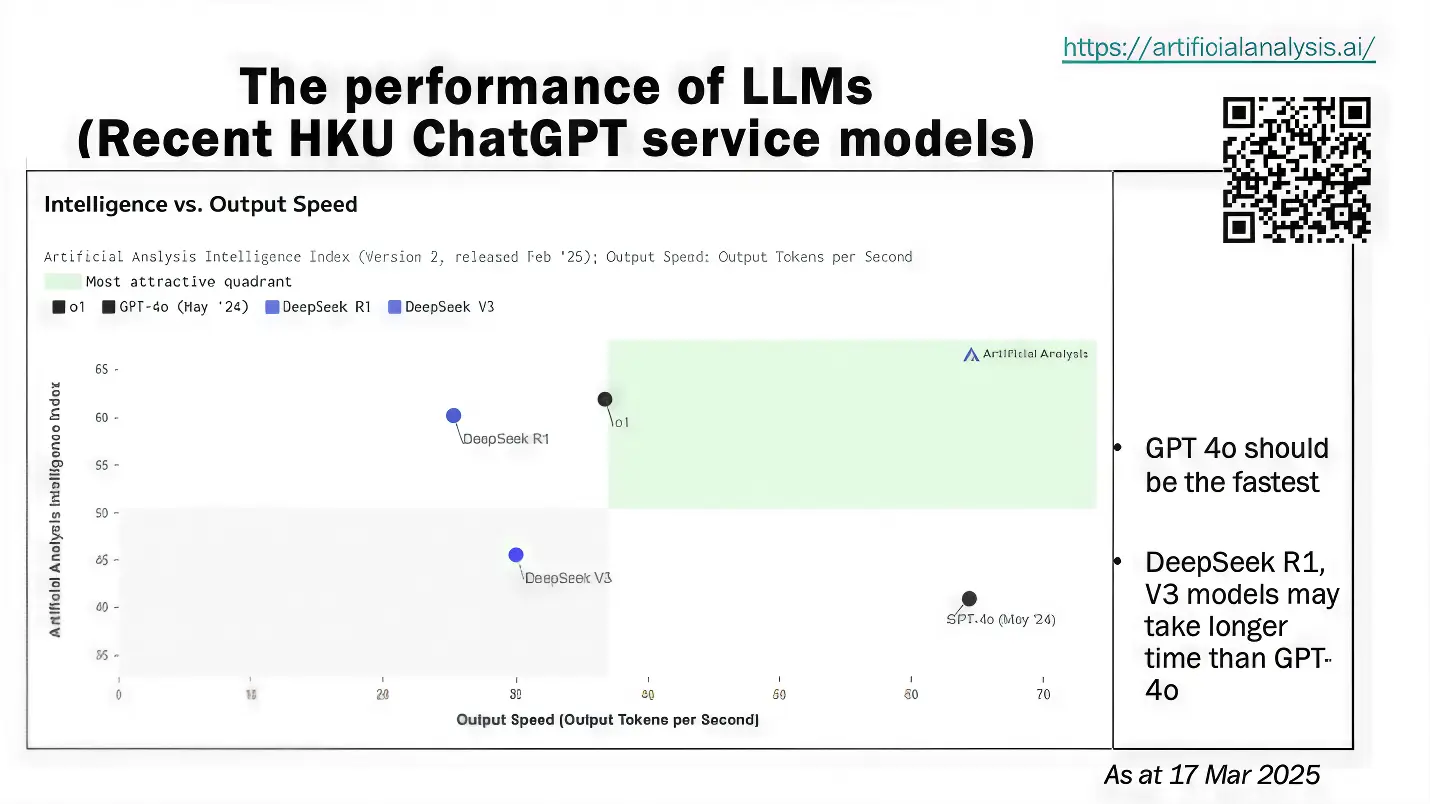
Performance is important. The most recent model of the web application, GPT-4o, outperforms DeepSeek R1 and V3 in terms of output speeds. For effective classroom use, this speed performance advantage can be helpful and pertinent.
The ChatGPT app, like any AI tool, has usage limits. Users can upload files up to a maximum file size of 3 MB, and only one file can be uploaded per minute. For larger documents, educators need to strategize, perhaps splitting documents into smaller parts or prioritizing uploads.
Prompting Techniques
Prompt engineering is the art of crafting effective prompts to elicit desired outputs from AI models. Cain (2023) describes prompt engineering as a “steering mechanism” of GenAI users. A 2024 article by McKinsey & Company defines it as “the practice of designing inputs for AI tools that will produce optimal outputs.” By strategically crafting prompts, a user not only improves the relevance of the information provided by an AI model, but also enhances the productivity and satisfaction of human-AI collaboration experience as one masters effective prompting techniques.
In AI prompting workshop, Dr. Carson Hung of TALIC discussed six key strategies for effective prompt engineering.
- Write clear instructions: Be specific and unambiguous in your instructions.
Provide reference text: Supplement your prompt with relevant context or examples. - Split complex tasks: Break down large tasks into smaller, more manageable subtasks.
- Give the model time to “think”: Allow sufficient processing time for complex tasks.
- Use external tools: Integrate external resources/tools to enhance the AI’s capabilities.
- Test changes systematically: Experiment and refine the prompts for optimal
results.
Beyond these strategies, effective prompting entails various tactics. These include: providing detailed context and specific information in your prompts; adopting a persona: (i.e., a historian, a research professor); and employing delimiters (i.e., quotes, double quotes, triple quotes and tags) to structure and clarify different parts of the prompt.
- Context Information: Including detailed context and specific information in your prompt.
- Adopting a Persona: Instructing the AI to respond as a specific persona (e.g., a historian, a journalist).
- Using Delimiters: Employing delimiters (e.g., quotes, tags) to structure and clarify different parts of the prompt. [Insert a slide image showcasing delimiter use here].
Integrating Prompt Engineering to Enhance Lesson Design

Prompt engineering can be integrated into the classroom to enhance the teaching and learning experience. By carefully crafting prompts, teachers can guide Al to produce tailored, relevant, and engaging content. ChatGPT is a powerful language model that can handle varied tasks from drafting, analyzing, and summarizing textual content, to translating, performing grammar checking, and more. However, to leverage Al effectively, it is important to provide clear and specific instructions detailing the context and specifics of the educational goal in crafting meaningful AI prompts.
In the prompting workshop, Ellen Seto of TALIC engaged teachers in two hands-on activities including collaboration with participants in writing an abstract for a student research paper, and preparing a summary for a grant proposal. The teachers who participated in the workshop were provided pre-designed “standardized prompts” to guide them to tailor their prompts to their own T&L context. The teachers experimented with different descriptive words, made changes to the AI persona, and applied delimiters to modify their prompts in ChatGPT based on the results they observed. They are able to evaluate whether the wordings that they applied in their prompts effectively express the intended results they desired to generate. Employing carefully crafted standard prompts supplemented with precise word definitions, roles and context descriptions as stated by Spasié and Jankovic (2023), has the potential to enhance the strategy design and lesson preparation of teachers who are working in collaboration with AI.
Challenges and Future Outlooks
ChatGPT is an evolving language model, it is not perfect and there are limitations to consider. ChatGPT’s answers are based directly on the prompt that a user provides, it is important to note that there may be potential biases based on how one phrases the prompt. It is important to fact check ChatGPT’s response because it can provide inaccurate, biased or outdated answers. In addition, the chatbot models also may not be trained with specific expert knowledge on highly specialised subjects. Hence, references and citations should always be checked for accuracy. AI Chatbot models also may not be able to provide the same level of human insight as a person on understanding cultural practices, human habits, slang and idioms etc. For those queries, human subjects are a source of more sensible answers.
AI tools such as ChatGPT, when used effectively, offer significant potential for enhancing teaching and learning. Even with the given restrictions associated with the use of artificial intelligence, effective prompt engineering gives teachers and students the ability to harness the immense potential of AI, which may elevate the learners interest and improve teaching and learning outcomes. What we are interested in learning most in the future is: How can we best enable teaching and learning through building AI-human partnerships?
Reference
- Cain, W. (2023). Prompting change: Exploring prompt engineering in large language model Al and its potential to trans- form education. TechTrends. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-023-00896-0
- Lee, D., & Palmer, E. (2025). Prompt engineering in higher education: a systematic review to help inform curricula. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 22(1), 7.
- Susnjak, T. (2023). Beyond predictive learning analytics modelling and onto explainable artificial intelligence with prescriptive analytics and ChatGPT. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-023-00336-3
- McKinsey & Company (2024, March 22). What is prompt engineering? https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-%20explainers/what-is-prompt-engineering#/
Ellen SETO
Senior Lecturer / Senior Instructional Designer
Teaching and Learning Innovation Centre



